XCP-ng Server Setup Best Practices
XCP-ng Server Setup Best Practices
 1. Hardware Planning
1. Hardware Planning
 General Hardware Both older and newer hardware are fine, as long as it is x86 and supports virtualization.
General Hardware Both older and newer hardware are fine, as long as it is x86 and supports virtualization. Software RAID Boot XCP-ng supports mdadm mirror setup on install
Software RAID Boot XCP-ng supports mdadm mirror setup on install Hardware RAID Controller Good for local storage management
Hardware RAID Controller Good for local storage management HBA or passthrough — Allows software (like ZFS or external storage) to manage redundancy. RAID controllers are not recommended when using passthrough to ZFS
HBA or passthrough — Allows software (like ZFS or external storage) to manage redundancy. RAID controllers are not recommended when using passthrough to ZFS Dual or more NICs — Separate management, VM, and storage traffic.
Dual or more NICs — Separate management, VM, and storage traffic.
 2. Install & Initial Config
2. Install & Initial Config
 Use the latest stable XCP-ng ISO — Stable builds ensure compatibility and security.
Use the latest stable XCP-ng ISO — Stable builds ensure compatibility and security. Set a static IP during install — Prevents DHCP surprises, especially for remote management and storage access.
Set a static IP during install — Prevents DHCP surprises, especially for remote management and storage access. Have a Host Naming Scheme — Simplifies management and XOA integration.
Have a Host Naming Scheme — Simplifies management and XOA integration.
 3. Security
3. Security
 The firewall is enabled by default — review and adjust if needed
The firewall is enabled by default — review and adjust if needed Disable SSH password authentication — Use SSH keys for access.
Disable SSH password authentication — Use SSH keys for access. Use VLANs or Separate Network — Limit exposure of management interfaces.
Use VLANs or Separate Network — Limit exposure of management interfaces. Apply updates to XCP-ng and XOA — Keep the host secure, stable, and get new features
Apply updates to XCP-ng and XOA — Keep the host secure, stable, and get new features
 4. Storage Setup
4. Storage Setup
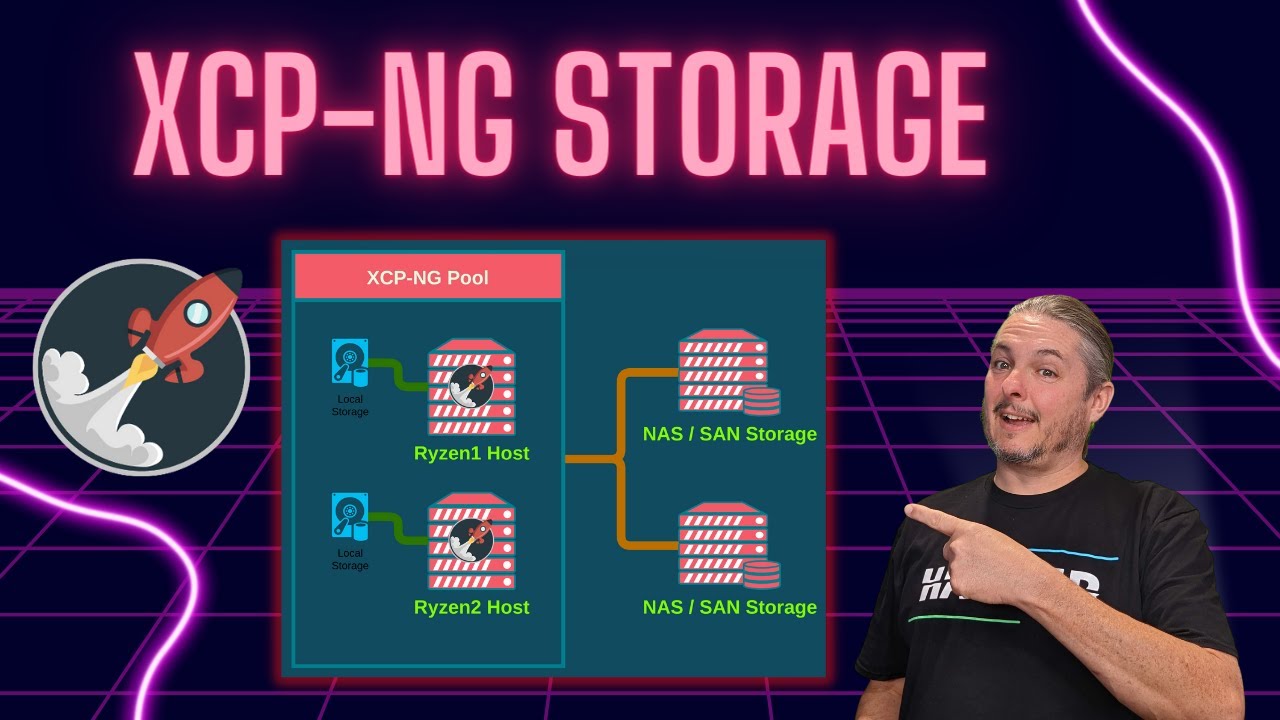
 Local Storage
Local Storage
 Use SSDs or NVMe for local SRs — Essential for high-performance workloads.
Use SSDs or NVMe for local SRs — Essential for high-performance workloads. Local ZFS this is supported but currently not managed via the XO interface
Local ZFS this is supported but currently not managed via the XO interface Prefer EXT over LVM Thin provisioned and not block based so it’s easier to manage and recover
Prefer EXT over LVM Thin provisioned and not block based so it’s easier to manage and recover
 External Storage
External Storage
 NFS is preferred over iSCSI
NFS is preferred over iSCSI
 Simpler integration with XCP-ng
Simpler integration with XCP-ng Easier to recover from because it is file based
Easier to recover from because it is file based Use MC-LAG switch setup for redundancy
Use MC-LAG switch setup for redundancy May be slightly lower performance than iSCSI in some edge cases
May be slightly lower performance than iSCSI in some edge cases
 iSCSI
iSCSI
 Multipath is supported
Multipath is supported Not thin provisioned
Not thin provisioned Block not file based
Block not file based
 Hyper Converged XOSTOR which is based on DRBD
Hyper Converged XOSTOR which is based on DRBD
 Storage is replicated across nodes, allowing VMs to survive host failures.
Storage is replicated across nodes, allowing VMs to survive host failures. No need for a dedicated external SAN/NAS—storage
No need for a dedicated external SAN/NAS—storage Heavy network dependency to sync hosts
Heavy network dependency to sync hosts Can have much higher latency on writes without performant hardware
Can have much higher latency on writes without performant hardware Only suitable when consistent, low-latency networking is available between nodes.
Only suitable when consistent, low-latency networking is available between nodes.
 5. VM Management Best Practices
5. VM Management Best Practices
 Use rational naming conventions — e.g.,
Use rational naming conventions — e.g., prod-app-01,lab-win10-02 Tag by role, department, and or environment — Useful for automation, filtering, and backups
Tag by role, department, and or environment — Useful for automation, filtering, and backups Storage Design — VMs are ideal for running compute workloads, but storage should be handled externally when practical. https://lawrence.video/storagedesign
Storage Design — VMs are ideal for running compute workloads, but storage should be handled externally when practical. https://lawrence.video/storagedesign Don’t Over-provision — Don’t overprovsion CPU or Memory
Don’t Over-provision — Don’t overprovsion CPU or Memory
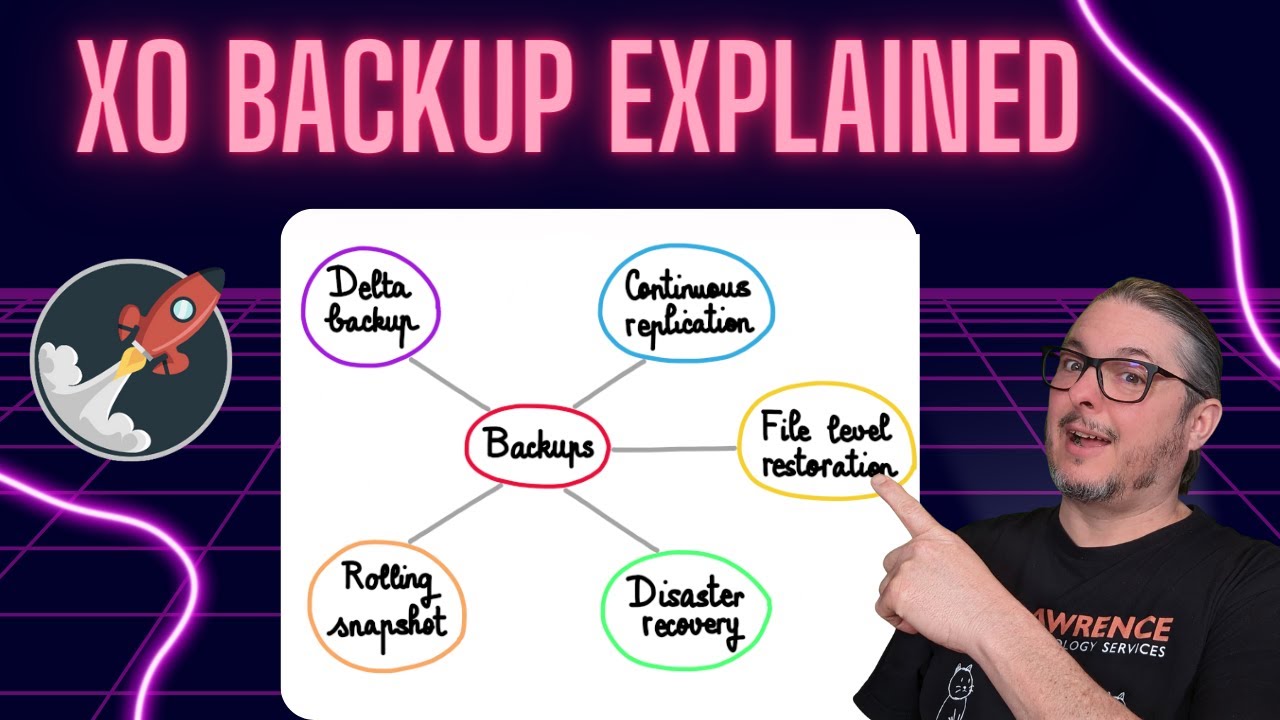
 6. Backup Strategy
6. Backup Strategy
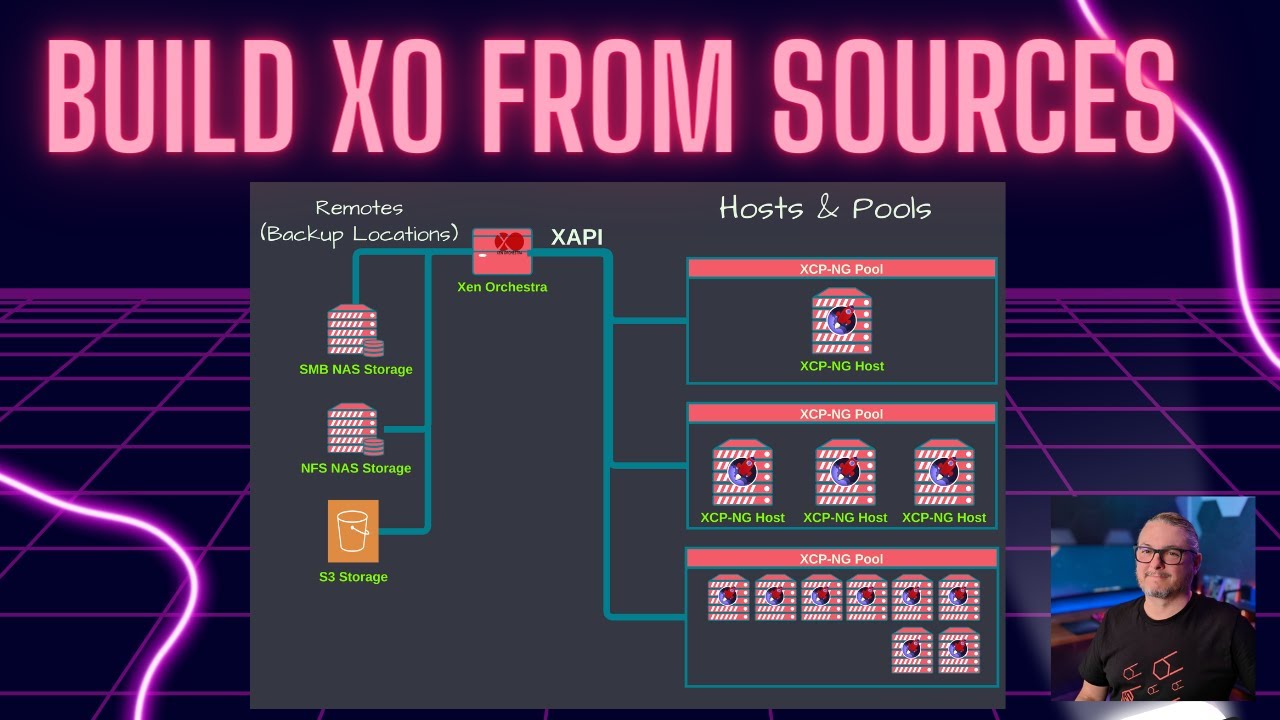
 Use XO backups — They are integrated and easily automated
Use XO backups — They are integrated and easily automated Keep backups on separate storage — Ideally not on the same NAS as the live NFS share
Keep backups on separate storage — Ideally not on the same NAS as the live NFS share Test your restores regularly — Because “successful backup” does not mean “tested restore”
Test your restores regularly — Because “successful backup” does not mean “tested restore”
 7. Networking
7. Networking
 Have a clear Naming Scheme — Take advantage of the descriptions field
Have a clear Naming Scheme — Take advantage of the descriptions field Name The Unused Interfaces — I name them “Not In Use”
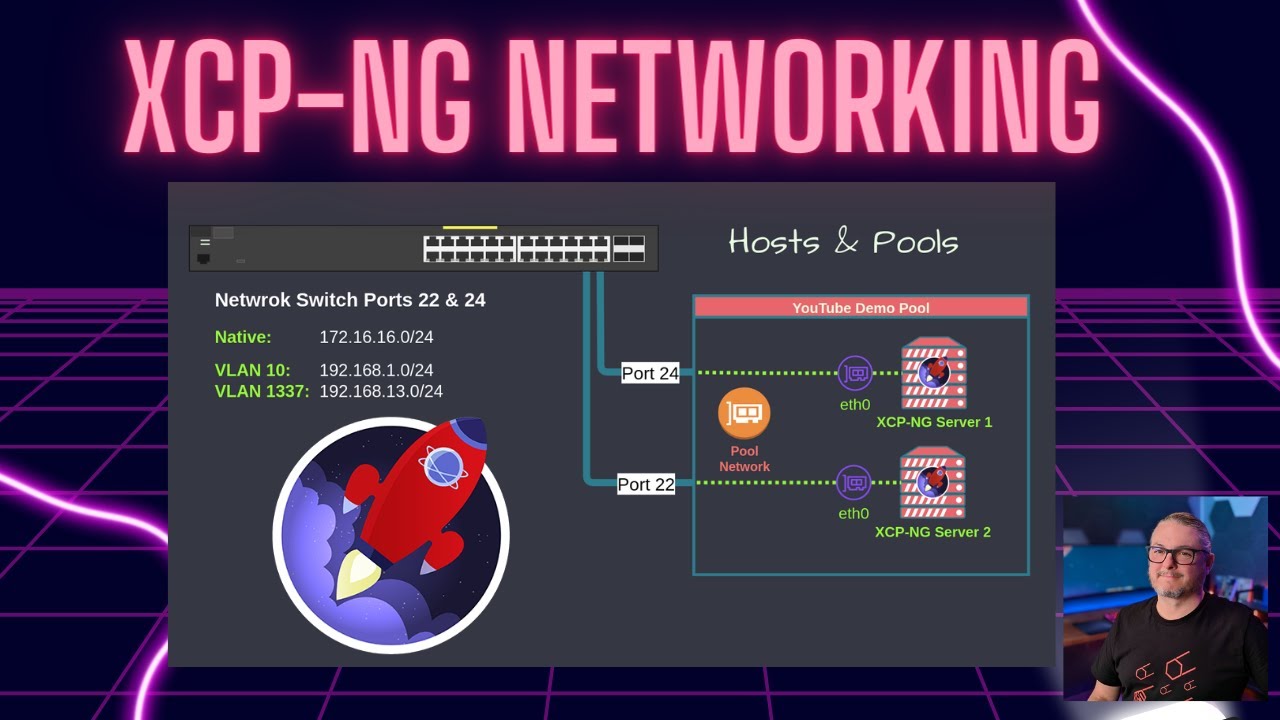
Name The Unused Interfaces — I name them “Not In Use” Segment management, VM, and storage traffic — Use VLANs or separate NICs
Segment management, VM, and storage traffic — Use VLANs or separate NICs Management Interface use a dedicate NIC if possible, not a bonded interface
Management Interface use a dedicate NIC if possible, not a bonded interface Bond NICs — Fully supported make sure your network switch does as well
Bond NICs — Fully supported make sure your network switch does as well Dedicated Backup, Storage, Migration Network — In XCP-ng, you can assign a default network for backup, storage, and migration traffic at the pool level.
Dedicated Backup, Storage, Migration Network — In XCP-ng, you can assign a default network for backup, storage, and migration traffic at the pool level.
 8. Monitoring & Maintenance
8. Monitoring & Maintenance
 Setup XO Email — Set up email notifications in XO
Setup XO Email — Set up email notifications in XO Use Syslog — Send data to a syslog server, I personally like Graylog
Use Syslog — Send data to a syslog server, I personally like Graylog
 9. Documentation & Scaling
9. Documentation & Scaling
 Keep a config doc or runbook — Include IPs, hostnames, pool members, etc..
Keep a config doc or runbook — Include IPs, hostnames, pool members, etc.. Use tags — For groupings like environment, function, or backup policies
Use tags — For groupings like environment, function, or backup policies Netbox Support — The Netbox plugin allows better IP and asset tracking for XCP-ng environments.
Netbox Support — The Netbox plugin allows better IP and asset tracking for XCP-ng environments.