ZFS Metadata & Cache Devices
| Component | What It Actually Does | Helps Most With | Common Use Cases | When It Usually Does Nothing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARC ( RAM Memory) | Primary read cache for data and metadata | All workloads | Everything | CACHE ALL THE THINGS |
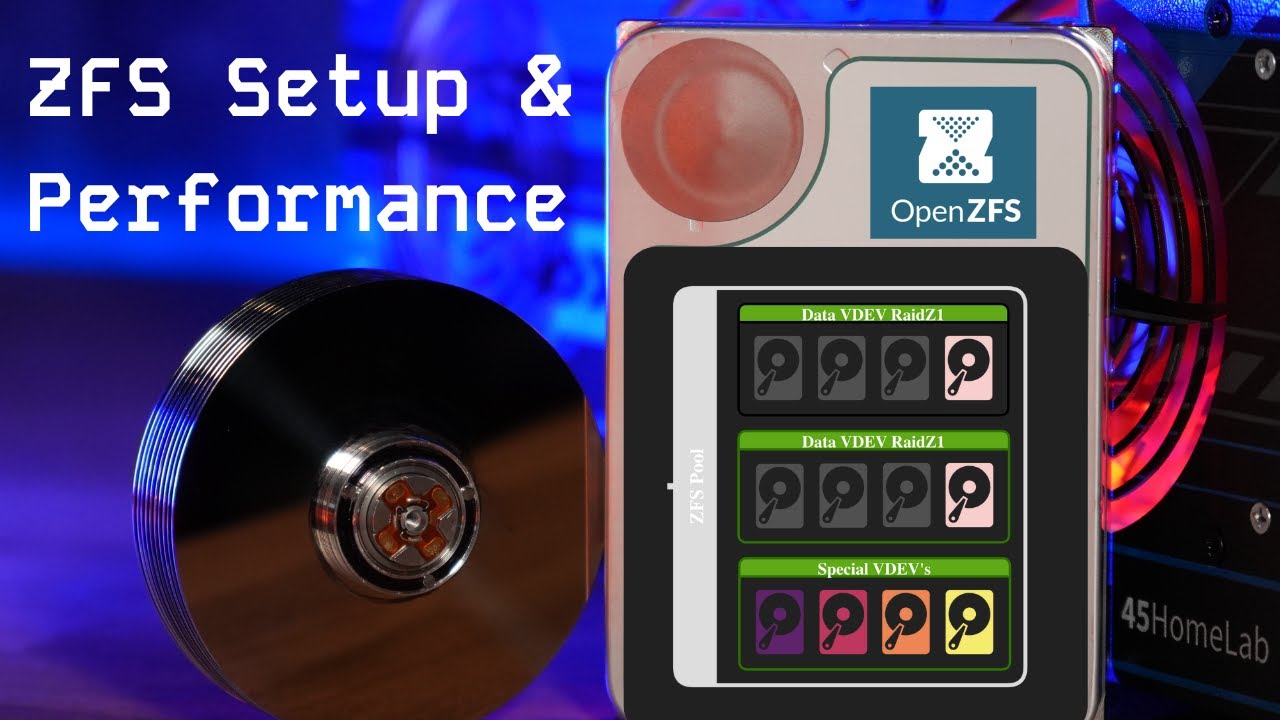
| VDEV Count | Determines IOPS and parallelism | Random I/O, concurrency | VMs, DBs, busy SMB | |
| Mirror VDEVs | Lowest latency, highest IOPS | Random I/O | Virtualization, databases, SMB | Large-file streaming |
| RAIDZ (Z1/Z2/Z3) | Capacity-efficient parity | Sequential throughput | Media, backups, archives | High-IOPS workloads |
| SLOG | Accelerates sync writes only | Sync write latency | NFS VMs, databases | SMB, media, backups |
| Special / Metadata VDEV | Stores metadata + small blocks | Metadata-heavy I/O | VMs, SMB, small files | Large media files |
| L2ARC | Secondary read cache | Repeated reads | VM boot storms | Workloads where the same files are not requested again |
| Deduplication (DEDUP) | Eliminates duplicate blocks globally | Space efficiency | VM clones, VDI images, Cloning Data | Media, backups, mixed data |
Deduplication – Special Notes (Read Before Enabling)
| Requirement | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Very high RAM | DDT must fit in memory for performance |
| Predictable data | Random data defeats dedupe |
| Metadata performance | DEDUP is metadata-heavy |
| Careful capacity planning | DDT grows fast and is hard to remove |
Storage Efficiency & Performance
Klara Systems: RAIDZ, Mirrors, and Hybrid Configurations
Klara Systems: Understanding ZFS vdev Types
Klara Systems: dRAID